 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| General description of IRIGB standard | This site is managed and sponsored by TIMELINK MICROSYSTEMS. > The European leader in IRIGB |
||||||||||||||||||
| Inter Range Instrumentation Group mod B | |||||||||||||||||||
| Communication systems, data handling systems, tracking and telemetry systems require time-of-the day information for data correlation with time.
Parallel and serial formatted time codes are used to efficiently interface the timing system to the user system. Parallel time codes are defined in IRIG standard 205-87. Standardization of time code is necessary to ensure system compatibility among the various ranges, ground networks, industrial projects and international cooperation. |
|||||||||||||||||||
| The IRIG standard 200-98, define IRIG serial time code formats. The characteristics of six serial time codes presently used are defined :A, B, D, E, G, H.
For a detailed presentation of these characteristics, download the pdf version of the IRIG standard : |
|||||||||||||||||||
| IRIGB standard 200-04, pdf file (372 Ko) | |||||||||||||||||||
| For a first introduction to IRIGB characteristics, we provide the main information through the two following figures : | |||||||||||||||||||
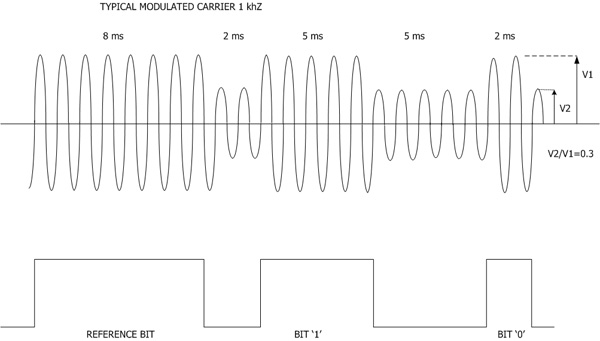 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| The figure below shows the IRIG format B: BCD time-of-the year in days, hours, minutes and seconds | |||||||||||||||||||
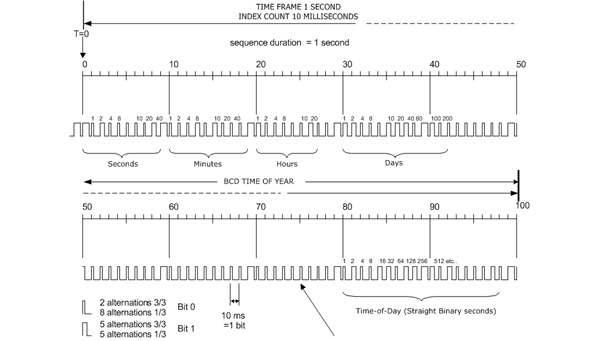 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Download the pdf version of this figure! | |||||||||||||||||||
| Home | IRIGB Standard | Products | Links | Contacts | |||||||||||||||